通过刷题学习到的数据结构。
1. 什么是Trie
Trie树的名字有很多,比如字典树,前缀树等等。 如下图:
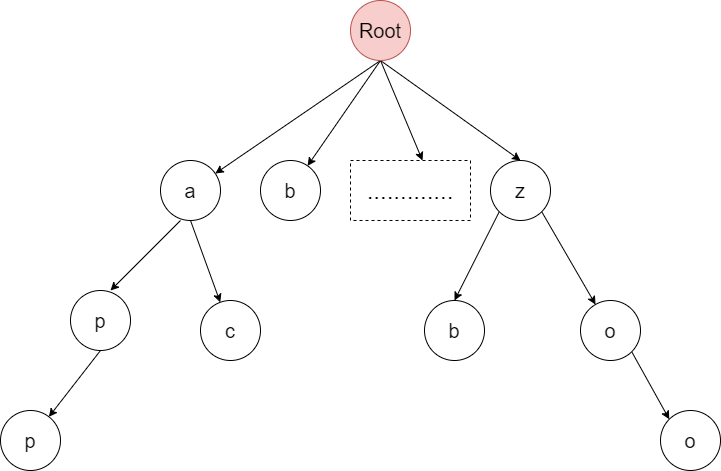
上图是一棵Trie,我们从上图已画出的节点来看,包含的集合有{“a”, “ap”,”app”, “ac”, “b”, “z”, “zb”, “zo”, “zoo”}
Trie的特点:
- 根节点不包含字符,除根节点外的每一个子节点都包含一个字符。
- 从根节点到某一节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,就是该节点对应的字符串。
- 每个单词的公共前缀作为一个字符节点保存。
通常会在节点结构中设置一个标志,用来标记该结点处是否构成一个单词(关键字)。
一般而言一个trie树的节点如果只统计小写的单词,那么它的节点需要有一个单词结尾的标志和26个孩子指针,其指针分别指向[a~z]。
2. Trie的作用
1. 词频统计。
可能有人会说,词频统计简单可以使用hash或者堆就可以逐个计数呀。但是这样会占用大量的空间,因为每个词都需要占用一定的空间。
如果内存有限呢?还能这么做吗?所以这里我们就可以通过使用Trie来压缩空间,因为公共前缀都是用一个节点保存的,这样就避免前缀的重复存储了,大大的节省了存储的空间。
2. 前缀匹配
就拿上面的图举例,如果我想获取所有以”a”开头的字符串,可以很快得到的是{“a”, “ap”, “app”, “ac”},如果不用trie,该怎么做呢?
最直接的办法就是暴力匹配,时间复杂度为O(N^2) ,那么用Trie就不一样了,它可以做到len,len为检索单词的长度,可以说这样就大大提升了搜索的效率。
3. 字符串排序
Trie树可以对大量字符串按字典序进行排序,思路也很简单:遍历一次所有关键字,将它们全部插入trie树,树的每个结点的所有儿子很显然地按照字母表排序,然后先序遍历输出Trie树中所有关键字即可。
正好leetcode上也有一道实现Trie的题目,连测试数据都不用写(窃喜)。
3. LeetCode 208
208. 实现 Trie (前缀树)
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含
insert,search, 和startsWith这三个操作。示例:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>
> trie.insert("apple");
> trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
> trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
> trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
> trie.insert("app");
> trie.search("app"); // 返回 true
>
说明:
- 你可以假设所有的输入都是由小写字母
a-z构成的。- 保证所有输入均为非空字符串。
思路: 上面已经通过性质说了很清楚了, 具体的细节我们在代码中通过注释的方式来说明。
1 | class Trie { |