在大二学习数据结构的时候已经学习过堆排序,当时只是理解的很浅,也没机会实现一次。自从开始做LeetCode后一直都在使用Priority_queue,今天有机会就来实现下。
堆排序(英语:Heapsort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆的性质:即子节点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。 (wiki给的解释)
堆:通常是可以被看作成一颗完全二叉树.通常满足下列性质:
(大顶堆)堆中孩子节点的值小于其父节点的值
(小顶堆)堆中的孩子节点的值大于其父节点的值
堆总是一个完全二叉树
堆就是用数组实现的完全二叉树,所以它没有使用父指针或者子指针。堆根据堆属性排序,堆属性决定了树中节点的位置。由于在数组中,根据数组的下标可以很快的获得当前节点的父节点或则是当前节点子节点。
- 当前节点的父节点
(i - 1) / 2 - 当前左孩子
(i * 2) + 1 - 当前右孩子
(i * 2) + 2

堆的用处:
- 构建优先队列
- 支持堆排序
- 快速找出一个集合中的最小值(或者最大值)
堆的插入
插入某元素完成后要继续保持堆的性质就必须对堆进行调整使其能够继续满足堆的性质.
如下图: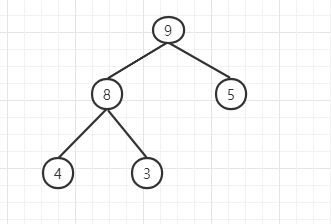
这个堆所对应的数组是{9, 8, 5, 4, 3}
我们插入一个新元素 7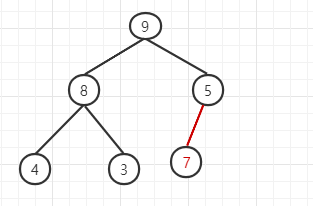
这个时候我们需要调用heapify()调整堆中节点使之成为
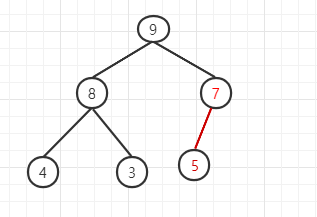
1 | void heapify(vector<int>& nums, int start, int n){ |
建堆
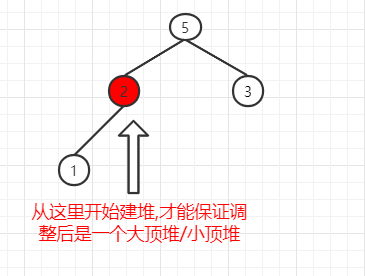
1 | void buildHeap(vector<int>& nums){ |
堆排序
1 | vector<int> heapSort(vector<int>& nums){ |
完整的代码
1 | class Solution { |