看了很多blog踩了很多坑,在此总结下。
CentOS7
1.下载apue源码
2. 解压
1 | tar -zxvf src.3e.tar.gz |
3. 复制到/usr/include
1 | cd ./apue.3e |
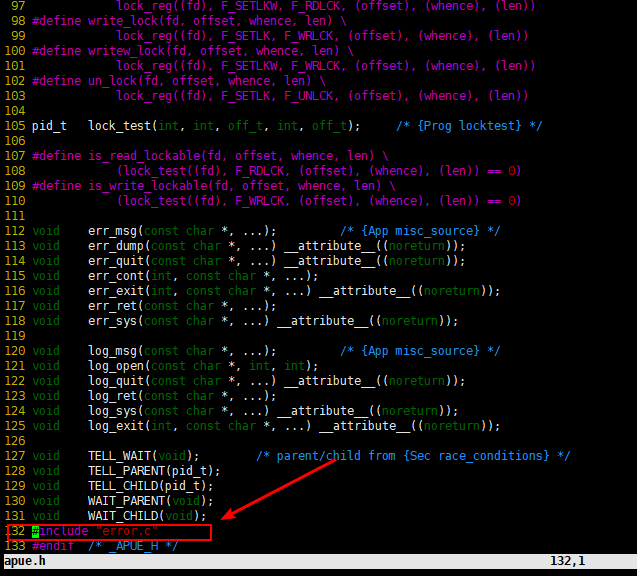
4. 修改/usr/include/apue.h
1 | cd /usr/include |
以上apue的环境就搭建完成了
Ubuntu
1.下载apue源码
2. 解压
1 | tar -zxvf src.3e.tar.gz |
3. 安装编译所需要的中间件
1 | sudo apt-get install libbsd-dev |
4. 执行make编译
1 | make |
5. 复制到/usr/include
1 | cd ./apue.3e |
6. 修改/usr/include/apue.h
1 | cd /usr/include |

以上apue的环境就搭建完成了
使用err_sys()等函数报未定义错误解决办法
err_sys和err_quit等函数并不是系统调用和库函数,而是作者自己编写的函数,需要自建一个.h文件将下面的代码补充上,并在每次使用上述函数的时候包含该文件。
例如:将改文件命名为apueerror.h ,将该头文件放在和apue.h同一个目录下(我的目录是/usr/include 。
每次使用apue中的函数的时候最好都包含进来
1 |
apueerror.h包含的代码如下:
1 |
|